Modelling medicanes
Understand the Dynamics: Advanced Modelling of Medicanes
Ocean and atmosphere models will be used to carry out the demonstration and impact studies activity foreseen during the MEDICANES project.
SHYFEM-WW3 Ocean Model
The hydrodynamic core is based on the System of HydrodYnamic Finite Element Modules (SHYFEM) code, an open-source unstructured ocean model for simulating hydrodynamics and transport processes at very high resolution. The model solves the shallow-water equations in their formulations with levels and transports using a finite element numerical method and semi-implicit time stepping. The wave modelling system developed will rely on the state-of-the-art spectral wave model WAVEWATCH III (WW3), which numerically solves the spectral wave energy density balance equation expressed in terms of the wave action density.
An unstructured and coupled hydrodynamic (SHYFEM) and wave (WW3) modelling system will be applied to simulate the sea conditions in the whole Mediterranean Sea during intense cyclones. SHYFEM and WW3 are coupled based on a so-called “hard coupling”, e.g. binding the models directly in the source code without any external coupling library. The benefit is minimal memory usage and very limited code changes in both models. Since both models use the same computational grid there is no need for spatial interpolation and the communication is done via global arrays that are assembled at the coupling interval between both models.
MESO-NH Atmospheric model
MESO-NH is a non-hydrostatic atmospheric model from the French research community initially developed by UT3 and Météo-France. Meso-NH has been widely used to study Mediterranean cyclones and intense convection over the past decades.
In the framework of MEDICANES, we will take profit of the various capabilities of Meso-NH by running simulations at very high resolution (large-eddy simulations) to investigate sub-km scale structures in windstorms and coupled simulations with the CROCO ocean model (Coastal and Regional Ocean COmmunity model ) and WW3 wave model (described above) to investigate complex interactions during compound events.
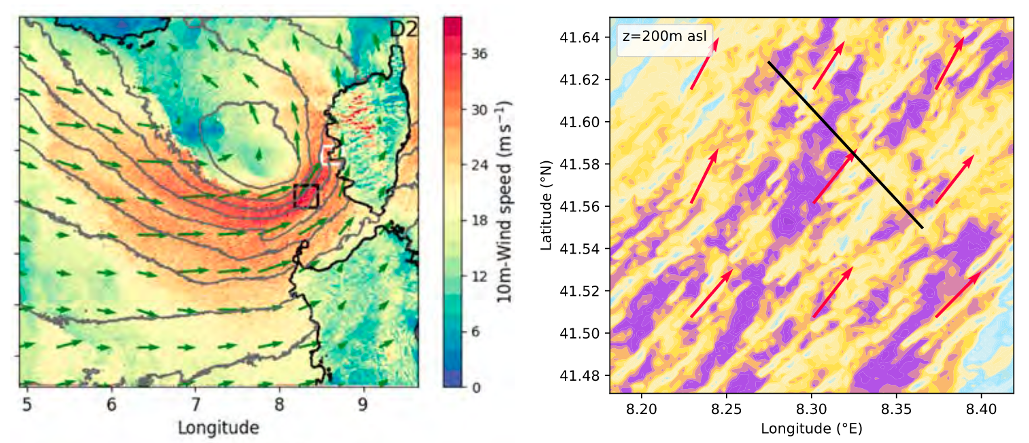 Wind speed in a large-eddy simulation of a Mediterranean cyclone with the Meso-NH model: full extent of the cyclone in the simulation domain (left) and fine-scale details in a zoom marked by the black square between Sardinia and Corsica (right). From Lfarh et al. (2023).
Wind speed in a large-eddy simulation of a Mediterranean cyclone with the Meso-NH model: full extent of the cyclone in the simulation domain (left) and fine-scale details in a zoom marked by the black square between Sardinia and Corsica (right). From Lfarh et al. (2023).
MOLOCH Atmospheric model
MOLOCH model is a non-hydrostatic, convection permitting model developed at CNR-ISAC where it also implemented for operational predictions at short-range (48 h), with grid spacing of about 1 km (https://www.isac.cnr.it/dinamica/projects/forecasts/). For research purposes, MOLOCH has been applied to the study of high impact weather events in the Mediterranean, such as cyclones, heavy precipitation, supercells and tornadoes, increasing the grid spacing up to 500 m. It is fully parallelized, applying the domain splitting technique, and particularly efficient, as demonstrated by comparison with other mesoscale models largely adopted.
In the framework of the MEDICANES project, MOLOCH will be used to simulate medicanes, following the experience gained in the framework of a Model Intercomparison exercise within the EU COST Action CA19109 “Medcyclones” devoted to the investigation of Mediterranean cyclones, also developing and applying assimilation techniques based on nudging, able to exploit satellite observations related with diabatic processes which are of crucial importance in the formation of these low pressure systems.
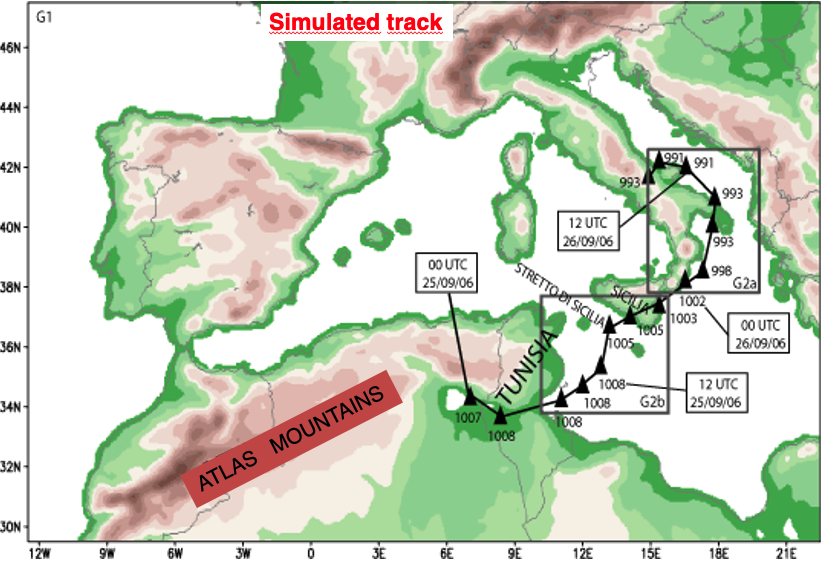 Simulate track for MARIA medicanes 25/09/2006 - Moscatello et al. (2008)
Simulate track for MARIA medicanes 25/09/2006 - Moscatello et al. (2008)
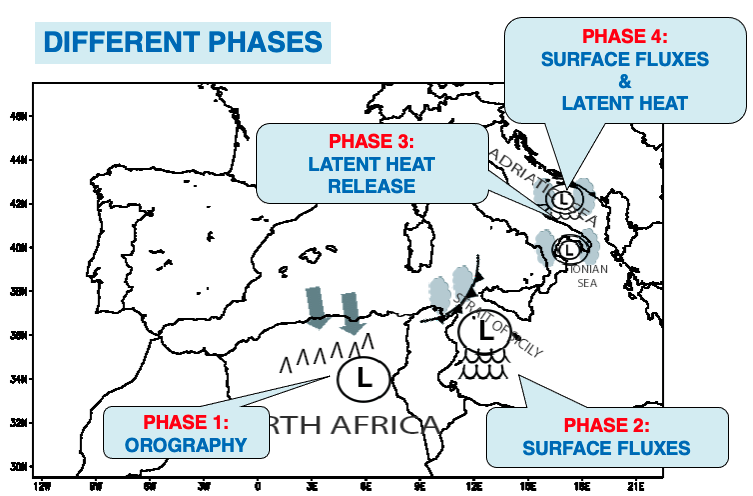 Different phase of MARIA medicanes 25/09/2006 - Moscatello et al. (2008)
Different phase of MARIA medicanes 25/09/2006 - Moscatello et al. (2008)
